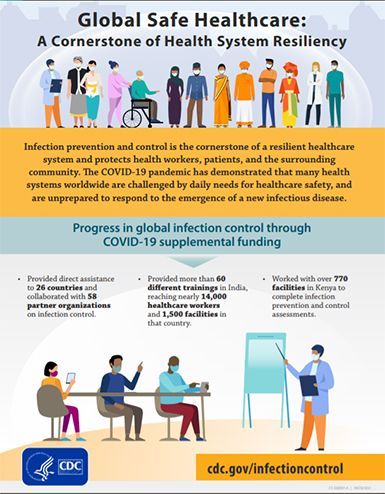
When it comes to global health, infectious diseases pose a significant threat to our societies. Outbreaks can spread rapidly, causing illness and death, and disrupting economies and everyday life. In recent years, we have witnessed the devastating impact of infectious diseases such as Ebola and COVID-19 on a global scale.
The Importance of Prevention
Prevention is crucial when it comes to combating infectious diseases. While advancements in medical treatments have improved our ability to handle outbreaks, it is far more effective to prevent these diseases from spreading in the first place. This is where robust strategies and technologies come into play.
Early Detection and Surveillance
To effectively prevent and respond to infectious diseases, early detection and surveillance systems are critical. Advanced technologies, such as big data analytics and artificial intelligence, enable the rapid detection of outbreaks by analyzing various data sources, including social media posts, news articles, and healthcare records. By identifying outbreaks early on, public health authorities can take immediate action to contain and mitigate the spread of the disease.
Vaccination Campaigns
Vaccination is one of the most successful strategies in preventing infectious diseases. Through effective campaigns, the population can build immunity against specific diseases, reducing the chances of an outbreak. With advancements in vaccine development and production, it is now possible to create vaccines for new diseases within a shorter timeframe, as exemplified by the remarkable speed at which COVID-19 vaccines were developed.
Additionally, public awareness campaigns are vital in dispelling misinformation and increasing vaccine acceptance within communities. Leveraging social media platforms, online campaigns, and celebrity endorsements can significantly improve public trust in vaccines, leading to higher vaccination rates and better disease prevention.
Hygiene and Sanitation Practices
Simple yet effective measures, such as maintaining good hygiene and sanitation practices, play a crucial role in preventing the spread of infectious diseases. Regular handwashing with soap and water, proper waste disposal, and access to clean water are essential for reducing the risk of transmission.
Technological innovations have also contributed to improving hygiene practices. Touchless technologies in public places, such as automatic sensors for taps and soap dispensers, minimize contact and reduce the potential for disease transmission. Additionally, advancements in water purification systems help ensure access to clean and safe water, particularly in regions where such resources are scarce.
Advancements in Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) plays a critical role in preventing the transmission of infectious diseases, especially in healthcare settings. Innovative designs, materials, and technologies have led to the development of more efficient and comfortable PPE. From high-quality masks to protective suits with improved breathability, these advancements not only enhance safety but also improve the overall experience for healthcare professionals.
Public Health Education and Communication
Education and communication are fundamental in shaping public behavior and attitudes towards infectious disease prevention. Clear and accurate information, delivered through various media channels, helps dispel myths and misconceptions, empowering individuals to make informed decisions regarding their health and that of their communities.
Virtual platforms and interactive tools can also play a significant role in disseminating public health information. Mobile applications, online platforms, and chatbots provide accessible and personalized guidance on disease prevention, symptom identification, and testing information.
Global Collaboration and Preparedness
Finally, global collaboration and preparedness are vital in ensuring a safer world. Sharing data, research, and resources among countries and international organizations strengthens our collective ability to prevent and respond to infectious diseases.
Investments in research and development are crucial to staying ahead of emerging infectious diseases. Rapid response teams, laboratory networks, and stockpiling of medical supplies contribute to a prepared and efficient approach to disease prevention and management.
Conclusion
Infectious disease prevention requires a multi-faceted approach, combining technological advancements, effective strategies, and global collaboration. With proactive measures in early detection, vaccination campaigns, hygiene practices, improved PPE, public health education, and preparedness, we can create a safer world for everyone. By focusing on prevention, we can minimize the devastating impact of infectious diseases and ensure a healthier future for generations to come.